Access 2010 Serial Port Control
The Cisco 2010 Connected Grid Router CGS 2010 is a rugged router optimized for use in the communication networks found in the energy and utility industries. Purple/v4/c4/21/80/c4218033-75ed-6ef8-e58a-7f133e54a62d/screen800x500.jpeg' alt='Access 2010 Serial Port Control' title='Access 2010 Serial Port Control' />
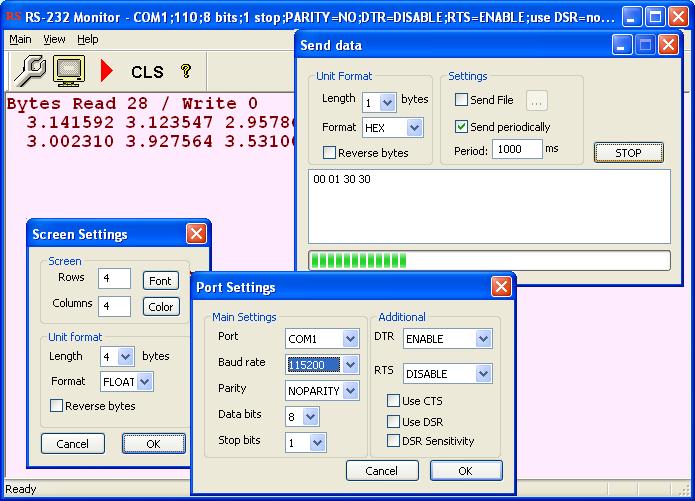 How to Do a Serial Loopback Test. A loopback test allows you to send and receive data from the same serial port to verify that the port is operational. To perform this test, you need to temporarily connect the proper pins to allow signals to be sent and received on the same port. Loopback Test. A loopback test can be used to troubleshoot serial communications. It can show problems in the serial port, the cable, or the software generating the messages without having to connect to third party hardware. By connecting the proper wires, a loopback test can verify the operation of serial communication. Loopback tests can be used for RS 2. RS 4. 22, and RS 4. For more information on RS 2. RS 4. 22, and RS 4. Serial Communication Overview. Note that not all serial devices, especially those with many connections on one card, allow hardware flow control on every serial output of the device. To perform a loopback test for RS 2. TXD pin must be connected to the RXD pin. This allows the data to flow from the transmit to the receive pins. Since the communication is differential for RS 4. RS 4. 85, the TXD connects to the RXD and the TXD connects to the RXD pins. A more advanced loopback test that allows hardware flow control will need more pins connected to allow the flow control signals to be properly passed. For RS 2.
How to Do a Serial Loopback Test. A loopback test allows you to send and receive data from the same serial port to verify that the port is operational. To perform this test, you need to temporarily connect the proper pins to allow signals to be sent and received on the same port. Loopback Test. A loopback test can be used to troubleshoot serial communications. It can show problems in the serial port, the cable, or the software generating the messages without having to connect to third party hardware. By connecting the proper wires, a loopback test can verify the operation of serial communication. Loopback tests can be used for RS 2. RS 4. 22, and RS 4. For more information on RS 2. RS 4. 22, and RS 4. Serial Communication Overview. Note that not all serial devices, especially those with many connections on one card, allow hardware flow control on every serial output of the device. To perform a loopback test for RS 2. TXD pin must be connected to the RXD pin. This allows the data to flow from the transmit to the receive pins. Since the communication is differential for RS 4. RS 4. 85, the TXD connects to the RXD and the TXD connects to the RXD pins. A more advanced loopback test that allows hardware flow control will need more pins connected to allow the flow control signals to be properly passed. For RS 2.  TMS320DM368 www. SPRS668CAPRIL 2010REVISED JUNE 2011 TMS320DM368 Digital Media SystemonChipDMSoC Check for Samples TMS320DM368 1 TMS320DM368 Digital. Advanced-Virtual-COM-Port_5.png' alt='Access 2010 Serial Port Control' title='Access 2010 Serial Port Control' />CTS and RTS pins must be connected along with the DTR and DSR pins. For RS 4. RS 4. 85, CTS should be connected to RTS and CTS should be connected to RTS. For more information about National Instruments serial interfaces, visit ni. Back to Top. 2. Connectors. DE 9 DB9 Connector. The DE 9 connector is the most common serial connector. This connector is found on National Instruments one and two port serial interfaces. Figure 1 Pinout diagram for DE 9 Connector To perform a loopback test with no hardware flow control, you will need to connect pins 2 and 3 for RS 2. RS 4. 224. 85. These connections can be seen in red below figure 2 for RS 2. RS 4. 224. 85. When using hardware flow control, you will need to connect pins 4 to 6 and 7 to 8 for RS 2. Pins 7 and 8 are used for RTSCTS hardware flow control where pins 4 and 6 are used for DTRDSR hardware flow control. For RS 4. Both of these connections are required for RTSCTS hardware flow control since RS 4. These connections can be seen in blue below figure 2 for RS 2. RS 4. 224. 85. Figure 2 RS 2. DE 9 plug with connections required for loopback test. Figure 3 RS 4. 224. DE 9 plug with connections required for loopback test. DB 2. 5 Connector. This connector is not as common as the DE 9 connector. This connector can still be used to perform a loopback test with a method similar to the one used for the DE 9 connector. Figure 4 Pinout diagram for DB 2. Connector. Most of the pins on DB 2. RS 2. 32, RS 4. RS 4. To perform a loopback test with no hardware flow control with a DB 2. RS 2. 32. For RS 4. The required connections can be seen in red on figures 5 and 6. Unlike many other virtualization solutions, its not particularly easy to connect a Windows 2008 HyperV guest to its host serial ports. Perversely, there are. Prepared by Kelly Buchanan Chief, Foreign, Comparative, and International Law Division I February 2013. Appendix Current State and Territory Firearms Legislation in. TemplateRefimprove This is a list of Internet socket port numbers used by protocols of the transport layer of the Internet Protocol Suite for the establishment of. For hardware flow control using RS 2. When using RS 4. This will allow the loopback test to use the proper flow control lines. These connections can be seen in blue on figures 5 and 6. Figure 5 RS 2. 32 female DB 2. Figure 6 RS 4. 224. DB 2. 5 plug with connections required for loopback test. P1. 0C RJ5. 0 Connector. This connector is most commonly found on National Instruments 4 port serial interfaces. The National Instrument 4 port serial interfaces come with 4 1. P1. 0C to DE 9 male converter cables. Figure 7 Pinout diagram for RJ5. Connector. It is not recommended to use the 1. P1. 0C connector by itself to perform a loopback test due to the small separation between pins. Using a 1. P1. 0C to DE 9 connector Part Number 1. Back to Top. 3. Performing a Loopback Test in Hyperterminal. Create a new connection with any name and icon. Select the communications port you would like to test. Select the type of flow control you would like to use. Note that Xon Xoff is software flow control and will only require that the TXD and RXD pins to be connected. Type a message using the computers keyboard. Any data that shows in Hyperterminal is received from the device. Back to Top. 4. Performing a Loopback test in Measurement Automation Explorer. Open Measurement Automation Explorer and select the communications port you would like to use. Ensure the proper settings are selected for flow control. Save the settings with the Save button and then click the Open VISA Test Panel button. Once the Test Panel window has opened, please select InputOutput. In the Basic IO tab, click the Query command to send the default IDNn command. The display window will then outline the write and read operations. The Test Panel should have successfully read the sent DNn command. Back to Top. 5. Performing a Loopback test in Lab. VIEWNote For a free evaluation copy of Lab. VIEW, visit ni. comtrylabview. Start Lab. VIEW2. Download Ultraman Fighting Evolution 3 Ps2 Iso Torrent. Select HelpFind Examples. Browse to Hardware Input and OutputSerialSimple Serial. Ensure the proper settings are selected and run the VI with the white run arrow on the toolbar. The Response indicator should display the DNList of Bluetooth profiles Wikipedia. In order to use Bluetooth technology, a device must be compatible with the subset of Bluetooth profiles often called services necessary to use the desired services. A Bluetooth profile is a specification regarding an aspect of Bluetooth based wireless communication between devices. It resides on top of the Bluetooth Core Specification and optionally additional protocols. While the profile may use certain features of the core specification, specific versions of profiles are rarely tied to specific versions of the core specification. For example, there are Hands Free Profile HFP 1. Bluetooth 2. 0 and Bluetooth 1. The way a device uses Bluetooth technology depends on its profile capabilities. The profiles provide standards which manufacturers follow to allow devices to use Bluetooth in the intended manner. For the Bluetooth low energy stack according to Bluetooth 4. At a minimum, each profile specification contains information on the following topics Dependencies on other formats. Suggested user interface formats. Specific parts of the Bluetooth protocol stack used by the profile. To perform its task, each profile uses particular options and parameters at each layer of the stack. This may include an outline of the required service record, if appropriate. This article summarizes the current definitions of profiles defined and adopted by the Bluetooth SIG and possible applications of each profile. Advanced Audio Distribution Profile A2. DPeditThis profile defines how multimedia audio can be streamed from one device to another over a Bluetooth connection it is also called Bluetooth Audio Streaming. For example, music can be streamed from a mobile phone, to a wireless headset, hearing aidcochlear implant streamer, car audio, or from a laptopdesktop to a wireless headset also, voice can be streamed from a microphone device to a recorder on a PC. The AudioVideo Remote Control Profile AVRCP is often used in conjunction with A2. DP for remote control on devices such as headphones, car audio systems, or stand alone speaker units. These systems often also implement Headset HSP or Hands Free HFP profiles for telephone calls, which may be used separately. The Best Of Hilary Duff Zip. Each A2. DP service, of possibly many, is designed to uni directionally transfer an audio stream in up to 2 channel stereo, either to or from the Bluetooth host. This profile relies on AVDTP and GAVDP. It includes mandatory support for the low complexity SBC codec not to be confused with Bluetooths voice signal codecs such as CVSDM, and supports optionally MPEG 1 Part 3MPEG 2 Part 3 MP2 and MP3, MPEG 2 Part 7MPEG 4 Part 3 AAC and HE AAC, and ATRAC, and is extensible to support manufacturer defined codecs, such as apt. X. 3Some Bluetooth stacks enforce the SCMS Tdigital rights management DRM scheme. In these cases, it is impossible to connect certain A2. DP headphones for high quality audio. Attribute Profile ATTeditThe ATT is a wire application protocol for the Bluetooth Low Energy specification. It is closely related to Generic Attribute Profile GATT. Bluetooth low energy Bluetooth LE, BLE, marketed as Bluetooth Smart1 is a wireless personal area network technology designed and marketed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group aimed at novel applications in the healthcare, fitness, beacons,2 security, and home entertainment industries. Compared to Classic Bluetooth, Bluetooth Smart is intended to provide considerably reduced power consumption and cost while maintaining a similar communication range. AudioVideo Remote Control Profile AVRCPeditThis profile is designed to provide a standard interface to control TVs, Hi fi equipment, etc. AV equipment to which a user has access. It may be used in concert with A2. DP or VDP. 4 It is commonly used in car navigation systems to control streaming Bluetooth audio. It also has the possibility for vendor dependent extensions. AVRCP has several versions with significantly increasing functionality 1. Basic remote control commands playpausestop, etc. The status of the music source playing, stopped, etc. Metadata information on the track itself artist, track name, etc. Browsing and manipulation of multiple players. Browsing of media metadata per media player, including a Now Playing list. Basic search capabilities. Support for Absolute volume. Number of items that are in a folder without downloading the list. Support for transmitting cover arts through the BIP over OBEX protocolFor example, this profile is used in Fitbit Blaze watch to control music. Basic Imaging Profile BIPeditThis profile is designed for sending images between devices and includes the ability to resize, and convert images to make them suitable for the receiving device. It may be broken down into smaller pieces Image Push. Usb Wireless Aircrack Download. Allows the sending of images from a device the user controls. Image Pull. Allows the browsing and retrieval of images from a remote device. Advanced Image Printingprint images with advanced options using the DPOF format developed by Canon, Kodak, Fujifilm, and Matsushita. Automatic Archive. Allows the automatic backup of all the new images from a target device. For example, a laptop could download all of the new pictures from a camera whenever it is within range. Remote Camera. Allows the initiator to remotely use a digital camera. For example, a user could place a camera on a tripod for a group photo, use their phone handset to check that everyone is in frame, and activate the shutter with the user in the photo. Remote Display. Allows the initiator to push images to be displayed on another device. For example, a user could give a presentation by sending the slides to a video projector. Basic Printing Profile BPPeditThis allows devices to send text, e mails, v. Cards, or other items to printers based on print jobs. It differs from HCRP in that it needs no printer specific drivers. This makes it more suitable for embedded devices such as mobile phones and digital cameras which cannot easily be updated with drivers dependent upon printer vendors. Common ISDN Access Profile CIPeditThis provides unrestricted access to the services, data and signalling that ISDN offers. Cordless Telephony Profile CTPeditThis is designed for cordless phones to work using Bluetooth. It is hoped that mobile phones could use a Bluetooth CTP gateway connected to a landline when within the home, and the mobile phone network when out of range. It is central to the Bluetooth SIGs 3 in 1 phone use case. Device ID Profile DIPeditThis profile allows a device to be identified above and beyond the limitations of the Device Class already available in Bluetooth. It enables identification of the manufacturer, product id, product version, and the version of the Device ID specification being met. It is useful in allowing a PC to identify a connecting device and download appropriate drivers. It enables similar applications to those the Plug and play specification allows. This is important in order to make best use of the features on the device identified. A few examples illustrating possible uses of this information are listed below 1. In PC to PC usage models such as conference table and file transfer, a PC may use this information to supplement information from other Bluetooth specifications to identify the right device to communicate with.
TMS320DM368 www. SPRS668CAPRIL 2010REVISED JUNE 2011 TMS320DM368 Digital Media SystemonChipDMSoC Check for Samples TMS320DM368 1 TMS320DM368 Digital. Advanced-Virtual-COM-Port_5.png' alt='Access 2010 Serial Port Control' title='Access 2010 Serial Port Control' />CTS and RTS pins must be connected along with the DTR and DSR pins. For RS 4. RS 4. 85, CTS should be connected to RTS and CTS should be connected to RTS. For more information about National Instruments serial interfaces, visit ni. Back to Top. 2. Connectors. DE 9 DB9 Connector. The DE 9 connector is the most common serial connector. This connector is found on National Instruments one and two port serial interfaces. Figure 1 Pinout diagram for DE 9 Connector To perform a loopback test with no hardware flow control, you will need to connect pins 2 and 3 for RS 2. RS 4. 224. 85. These connections can be seen in red below figure 2 for RS 2. RS 4. 224. 85. When using hardware flow control, you will need to connect pins 4 to 6 and 7 to 8 for RS 2. Pins 7 and 8 are used for RTSCTS hardware flow control where pins 4 and 6 are used for DTRDSR hardware flow control. For RS 4. Both of these connections are required for RTSCTS hardware flow control since RS 4. These connections can be seen in blue below figure 2 for RS 2. RS 4. 224. 85. Figure 2 RS 2. DE 9 plug with connections required for loopback test. Figure 3 RS 4. 224. DE 9 plug with connections required for loopback test. DB 2. 5 Connector. This connector is not as common as the DE 9 connector. This connector can still be used to perform a loopback test with a method similar to the one used for the DE 9 connector. Figure 4 Pinout diagram for DB 2. Connector. Most of the pins on DB 2. RS 2. 32, RS 4. RS 4. To perform a loopback test with no hardware flow control with a DB 2. RS 2. 32. For RS 4. The required connections can be seen in red on figures 5 and 6. Unlike many other virtualization solutions, its not particularly easy to connect a Windows 2008 HyperV guest to its host serial ports. Perversely, there are. Prepared by Kelly Buchanan Chief, Foreign, Comparative, and International Law Division I February 2013. Appendix Current State and Territory Firearms Legislation in. TemplateRefimprove This is a list of Internet socket port numbers used by protocols of the transport layer of the Internet Protocol Suite for the establishment of. For hardware flow control using RS 2. When using RS 4. This will allow the loopback test to use the proper flow control lines. These connections can be seen in blue on figures 5 and 6. Figure 5 RS 2. 32 female DB 2. Figure 6 RS 4. 224. DB 2. 5 plug with connections required for loopback test. P1. 0C RJ5. 0 Connector. This connector is most commonly found on National Instruments 4 port serial interfaces. The National Instrument 4 port serial interfaces come with 4 1. P1. 0C to DE 9 male converter cables. Figure 7 Pinout diagram for RJ5. Connector. It is not recommended to use the 1. P1. 0C connector by itself to perform a loopback test due to the small separation between pins. Using a 1. P1. 0C to DE 9 connector Part Number 1. Back to Top. 3. Performing a Loopback Test in Hyperterminal. Create a new connection with any name and icon. Select the communications port you would like to test. Select the type of flow control you would like to use. Note that Xon Xoff is software flow control and will only require that the TXD and RXD pins to be connected. Type a message using the computers keyboard. Any data that shows in Hyperterminal is received from the device. Back to Top. 4. Performing a Loopback test in Measurement Automation Explorer. Open Measurement Automation Explorer and select the communications port you would like to use. Ensure the proper settings are selected for flow control. Save the settings with the Save button and then click the Open VISA Test Panel button. Once the Test Panel window has opened, please select InputOutput. In the Basic IO tab, click the Query command to send the default IDNn command. The display window will then outline the write and read operations. The Test Panel should have successfully read the sent DNn command. Back to Top. 5. Performing a Loopback test in Lab. VIEWNote For a free evaluation copy of Lab. VIEW, visit ni. comtrylabview. Start Lab. VIEW2. Download Ultraman Fighting Evolution 3 Ps2 Iso Torrent. Select HelpFind Examples. Browse to Hardware Input and OutputSerialSimple Serial. Ensure the proper settings are selected and run the VI with the white run arrow on the toolbar. The Response indicator should display the DNList of Bluetooth profiles Wikipedia. In order to use Bluetooth technology, a device must be compatible with the subset of Bluetooth profiles often called services necessary to use the desired services. A Bluetooth profile is a specification regarding an aspect of Bluetooth based wireless communication between devices. It resides on top of the Bluetooth Core Specification and optionally additional protocols. While the profile may use certain features of the core specification, specific versions of profiles are rarely tied to specific versions of the core specification. For example, there are Hands Free Profile HFP 1. Bluetooth 2. 0 and Bluetooth 1. The way a device uses Bluetooth technology depends on its profile capabilities. The profiles provide standards which manufacturers follow to allow devices to use Bluetooth in the intended manner. For the Bluetooth low energy stack according to Bluetooth 4. At a minimum, each profile specification contains information on the following topics Dependencies on other formats. Suggested user interface formats. Specific parts of the Bluetooth protocol stack used by the profile. To perform its task, each profile uses particular options and parameters at each layer of the stack. This may include an outline of the required service record, if appropriate. This article summarizes the current definitions of profiles defined and adopted by the Bluetooth SIG and possible applications of each profile. Advanced Audio Distribution Profile A2. DPeditThis profile defines how multimedia audio can be streamed from one device to another over a Bluetooth connection it is also called Bluetooth Audio Streaming. For example, music can be streamed from a mobile phone, to a wireless headset, hearing aidcochlear implant streamer, car audio, or from a laptopdesktop to a wireless headset also, voice can be streamed from a microphone device to a recorder on a PC. The AudioVideo Remote Control Profile AVRCP is often used in conjunction with A2. DP for remote control on devices such as headphones, car audio systems, or stand alone speaker units. These systems often also implement Headset HSP or Hands Free HFP profiles for telephone calls, which may be used separately. The Best Of Hilary Duff Zip. Each A2. DP service, of possibly many, is designed to uni directionally transfer an audio stream in up to 2 channel stereo, either to or from the Bluetooth host. This profile relies on AVDTP and GAVDP. It includes mandatory support for the low complexity SBC codec not to be confused with Bluetooths voice signal codecs such as CVSDM, and supports optionally MPEG 1 Part 3MPEG 2 Part 3 MP2 and MP3, MPEG 2 Part 7MPEG 4 Part 3 AAC and HE AAC, and ATRAC, and is extensible to support manufacturer defined codecs, such as apt. X. 3Some Bluetooth stacks enforce the SCMS Tdigital rights management DRM scheme. In these cases, it is impossible to connect certain A2. DP headphones for high quality audio. Attribute Profile ATTeditThe ATT is a wire application protocol for the Bluetooth Low Energy specification. It is closely related to Generic Attribute Profile GATT. Bluetooth low energy Bluetooth LE, BLE, marketed as Bluetooth Smart1 is a wireless personal area network technology designed and marketed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group aimed at novel applications in the healthcare, fitness, beacons,2 security, and home entertainment industries. Compared to Classic Bluetooth, Bluetooth Smart is intended to provide considerably reduced power consumption and cost while maintaining a similar communication range. AudioVideo Remote Control Profile AVRCPeditThis profile is designed to provide a standard interface to control TVs, Hi fi equipment, etc. AV equipment to which a user has access. It may be used in concert with A2. DP or VDP. 4 It is commonly used in car navigation systems to control streaming Bluetooth audio. It also has the possibility for vendor dependent extensions. AVRCP has several versions with significantly increasing functionality 1. Basic remote control commands playpausestop, etc. The status of the music source playing, stopped, etc. Metadata information on the track itself artist, track name, etc. Browsing and manipulation of multiple players. Browsing of media metadata per media player, including a Now Playing list. Basic search capabilities. Support for Absolute volume. Number of items that are in a folder without downloading the list. Support for transmitting cover arts through the BIP over OBEX protocolFor example, this profile is used in Fitbit Blaze watch to control music. Basic Imaging Profile BIPeditThis profile is designed for sending images between devices and includes the ability to resize, and convert images to make them suitable for the receiving device. It may be broken down into smaller pieces Image Push. Usb Wireless Aircrack Download. Allows the sending of images from a device the user controls. Image Pull. Allows the browsing and retrieval of images from a remote device. Advanced Image Printingprint images with advanced options using the DPOF format developed by Canon, Kodak, Fujifilm, and Matsushita. Automatic Archive. Allows the automatic backup of all the new images from a target device. For example, a laptop could download all of the new pictures from a camera whenever it is within range. Remote Camera. Allows the initiator to remotely use a digital camera. For example, a user could place a camera on a tripod for a group photo, use their phone handset to check that everyone is in frame, and activate the shutter with the user in the photo. Remote Display. Allows the initiator to push images to be displayed on another device. For example, a user could give a presentation by sending the slides to a video projector. Basic Printing Profile BPPeditThis allows devices to send text, e mails, v. Cards, or other items to printers based on print jobs. It differs from HCRP in that it needs no printer specific drivers. This makes it more suitable for embedded devices such as mobile phones and digital cameras which cannot easily be updated with drivers dependent upon printer vendors. Common ISDN Access Profile CIPeditThis provides unrestricted access to the services, data and signalling that ISDN offers. Cordless Telephony Profile CTPeditThis is designed for cordless phones to work using Bluetooth. It is hoped that mobile phones could use a Bluetooth CTP gateway connected to a landline when within the home, and the mobile phone network when out of range. It is central to the Bluetooth SIGs 3 in 1 phone use case. Device ID Profile DIPeditThis profile allows a device to be identified above and beyond the limitations of the Device Class already available in Bluetooth. It enables identification of the manufacturer, product id, product version, and the version of the Device ID specification being met. It is useful in allowing a PC to identify a connecting device and download appropriate drivers. It enables similar applications to those the Plug and play specification allows. This is important in order to make best use of the features on the device identified. A few examples illustrating possible uses of this information are listed below 1. In PC to PC usage models such as conference table and file transfer, a PC may use this information to supplement information from other Bluetooth specifications to identify the right device to communicate with.